What is skin cancer?
Skin cancer is a group of skin cells that have been damaged in a way that results in uncontrolled growth. Depending on the type of skin cancer, this can result in spread to distant sites in the body or locally destructive growth. Either forms of spread can result in damage to the body and eventual death if not treated.
Skin cancer are caused due to the abnormal growth of skin cells, most often developing on skin exposed to the sun. Melanoma is the most dangerous form of skin cancer and can spread rapidly to other parts of the body if not treated early. Understanding the symptoms and treatments related to melanoma is crucial for effective cancer care.
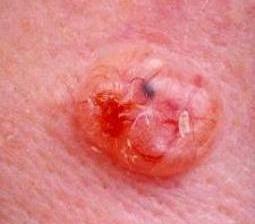
Type of Skin Cancer
There are various forms of skin cancer that individuals may develop. Melanoma cancer is the most common type of cancer that starts in the melanocytes, the cells that give skin its colour. It is less common than basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, which are the most prevalent types of skin cancer.
Overview of Different Types of Skin Cancer
The main types of skin cancer in the world include basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are known as non-melanoma skin cancers, originating in the top layer of the skin.
Understanding Melanoma
Melanoma is a type of cancer that develops from the pigment-containing cells in the skin. It is considered the most serious form of skin cancer due to its ability to spread quickly to other organs if not treated early.
Main Types of Skin Cancer
Basal and squamous cell carcinoma are the primary forms of skin cancer, accounting for the highest rates of skin cancer worldwide. While they are generally less aggressive than melanoma, early detection and treatment are still essential. These are very common types of skin cancers.
What Causes Skin Cancer?
The development of skin cancer is often linked to prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds. Factors such as frequent sunburns, light skin complexion, and a family history of skin cancer can contribute to the risk of developing common cancer.
Factors that Contribute to Skin Cancer Development
Various factors can increase the likelihood of developing skin cancer, including a weakened immune system, exposure to carcinogens, and genetic predisposition. Understanding these risk factors is crucial in preventing skin cancer.
How Skin Cancer Develops in Skin Cells
Skin cancer can arise when DNA damage occurs in skin cells, leading to uncontrolled growth and tumour formation. The mutations that drive skin cancer can be triggered by UV radiation, chemicals, or inherited genetic conditions.
Role of UV Radiation in Skin Cancer Formation
UV radiation from the sun is a major contributing factor to the development of skin cancer. Prolonged exposure to UV rays can damage the DNA in skin cells, increasing the risk of mutations that can lead to skin cancer over time.
Skin Cancer Prevention
Preventing skin cancer involves taking proactive measures to safeguard your skin from harmful UV radiation and other risk factors. Regular skin checks and sun protection are key components of skin cancer prevention.
Tips to Protect Your Skin from Skin Cancer
Protecting your skin from the sun's harmful rays by using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and seeking shade during peak hours can help reduce the risk of developing skin cancer. It is essential to be mindful of sun exposure, especially for individuals with fair skin.
Importance of Regular Skin Checks
Regular skin checks, including self-examinations and dermatologist assessments, play a vital role in the early detection of skin cancer. Identifying suspicious moles or skin lesions promptly can lead to timely intervention and improved treatment outcomes.
Understanding the Link Between Sun Exposure and Skin Cancer
The connection between sun exposure and skin cancer is well-established, with UV radiation being a known carcinogen. Limiting sun exposure, wearing protective clothing, and using sunscreen are essential strategies for reducing the risk of skin cancer.
Skin Cancer Diagnosis
Diagnosing skin cancer involves a series of evaluations and tests to determine the presence of cancerous cells in the skin. Medical professionals use various diagnostic methods, including biopsies and imaging techniques, to confirm the diagnosis of skin cancer.
How Skin Cancer Is Diagnosed
Physicians typically conduct a visual examination of the skin to identify suspicious growths or changes in moles that may indicate skin cancer. Further diagnostic procedures, such as dermoscopy or biopsy, may be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Diagnostic Tests for Skin Cancer
Diagnostic tests such as skin biopsies, imaging scans, and blood tests are utilised to detect and characterise skin cancer. These tests help healthcare providers determine the extent of the cancer and plan an appropriate course of treatment.
Role of Biopsy in Confirming Skin Cancer
A biopsy is a common procedure used to gather tissue samples from suspicious skin lesions for laboratory analysis. The results of a skin biopsy can confirm the presence of cancerous cells and provide crucial information for determining the type and stage of skin cancer.
Skin Cancer Treatments
The treatment of skin cancer varies depending on the type, stage, and location of the cancerous growths. Common treatment modalities include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapy.
Main Treatments for Different Types of Skin Cancer
Each type of skin cancer may require a specific treatment approach tailored to the individual's condition. Surgery, radiation therapy, and systemic treatments like immunotherapy are among the mainstay options for managing skin cancer effectively.
Surgery as a Common Skin Cancer Treatment
Surgical procedures such as excision, Mohs surgery, and lymph node dissection are commonly used to remove cancerous lesions and prevent the spread of skin cancer. Surgery is often recommended for early-stage skin cancers with defined borders.
Role of Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy in Skin Cancer Treatment
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy are systemic treatments that target cancer cells throughout the body. These therapies may be recommended for advanced skin cancers or as adjuvant treatments following surgery to eliminate any remaining cancer cells.


 Prevention Tips
Prevention Tips Early Detection
Early Detection Understanding Skin Cancer
Understanding Skin Cancer Success Stories
Success Stories Lifestyle and Skin Health
Lifestyle and Skin Health Advances in Treatment
Advances in Treatment Community & Events
Community & Events For Families
For Families What's Happening at Melanoma Scan?
What's Happening at Melanoma Scan?