Some Skin Cancer Frequently Asked Questions
What is skin cancer?
Skin cancer is a group of skin cells that have been damaged in a way that results in uncontrolled growth. Depending on the type of skin cancer, this can result in spread to distant sites in the body or locally destructive growth. Either forms of spread can result in damage to the body and eventual death if not treated.
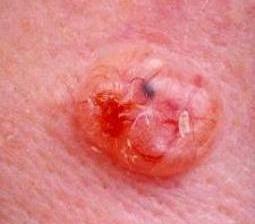
What causes skin cancer?
The vast majority of skin cancers are caused by exposure to ultraviolet light in the form of sun exposure but also from artificial sources such as solariums and arc welding. Other causes of skin cancer include exposure to cancer causing chemicals such as arsenic, or ionising radiation. These causes are much less common than ordinary sunburn from the sun. Many Australians are burnt on a regular basis, and sunburns are often associated with outdoor activities we spend our leisure time doing, such as outdoor sports, gardening and swimming. Many outdoor workers are also burnt frequently although workplace health and safety prevention has helped to some degree.

What is sun burn and how can I prevent it?
Sunburn is the reaction of your skin to exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun. Depending on your skin type and the season, sunburn can occur after as little as ten minutes of sun exposure if adequate protection is not provided. Fair skin types and people with light coloured hair and eyes are the most prone to sun burn and hence to the subsequent development of skin cancer. Most Australians are aware of the danger of sun exposure, but sun burn is still very common because people underestimate the amount of ultraviolet radiation they are exposing themselves to. This includes days when it is overcast, cooler or windy, when the burning effects of the sun may not be noticed before a sunburn has already happened. All sunburns cause damage to the cells of your skin, and these changes include damage to the DNA of your cells. Over many years, enough damage to the DNA of your cells can accumulate to cause a skin cancer to develop. Many older people experience skin cancers many years after the activities that caused them have stopped, and may continue to have skin cancers appear from time to time despite minimal sun exposure.
Prevention of sun burn is through covering your skin with clothing, hats and sunglasses or through the use of sunscreens at all times when ultraviolet light is intense enough to damage your skin. This is typically between 10am and 3pm although this varies with season and climate. Here in Queensland in the summer months the UV index may be extreme from early morning though to early evening


 Prevention Tips
Prevention Tips Early Detection
Early Detection Understanding Skin Cancer
Understanding Skin Cancer Success Stories
Success Stories Lifestyle and Skin Health
Lifestyle and Skin Health Advances in Treatment
Advances in Treatment Community & Events
Community & Events For Families
For Families What's Happening at Melanoma Scan?
What's Happening at Melanoma Scan?