Sun Damage
-
What causes skin cancer?
What causes skin cancer?
The vast majority of skin cancers are caused by exposure to ultraviolet light in the form of sun exposure but also from artificial sources such as solariums and arc welding. Other causes of skin cancer include exposure to cancer causing chemicals such as arsenic, or ionising radiation. These causes are much less common than ordinary sunburn from the sun. There are many types of skin cancers. Many Australians are burnt on a regular basis, and sunburns are often associated with outdoor activities we spend our leisure time doing, such as outdoor sports, gardening and swimming. Many outdoor workers are also burnt frequently although workplace health and safety preventionhas helped to some degree.
Understanding Skin Cancer: Risk Factors and Cancer Council
Skin cancer is a prevalent form of cancer that affects millions of people worldwide. Understanding the risk factors associated with this disease is crucial for prevention and early detection. The Cancer Council plays a vital role in raising awareness about skin cancer and promoting sun protection practices.
What is Skin Cancer?
Skin cancer is a type of cancer that originates in the skin cells. It can manifest in various forms, with the most common types being basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. These cancers often present with distinct signs that should not be ignored.
Definition of skin cancer
Skin cancer is characterised by the abnormal growth of skin cells, often triggered when you are exposed to uv radiation.
Different Types of skin cancer
The main types of skin cancer include basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma, each with its own characteristics and treatment options.
Common signs of skin cancer
Signs of skin cancer may include changes in skin growth, the appearance of new moles, or unusual skin discoloration. It is essential to regularly check your skin for any abnormalities.
What Are the Risk Factors for Skin Cancer?
You can get skin cancer from prolonged exposure to UV rays. UV radiation is a significant risk factor for the development of skin cancer. Prolonged exposure to UV rays, whether from the sun or tanning beds, can increase the likelihood of developing the disease.
UV radiation and skin cancer
UV radiation emitted by the sun or artificial sources can damage the DNA in skin cells, leading to mutations that may promote the growth of cancerous cells.
Skin type and skin cancer risk
Individuals with fair skin are at a higher risk of developing skin cancer compared to those with darker skin tones. Light-skinned individuals have less natural protection against UV radiation.
Exposure to UV radiation and skin cancer risk
Prolonged exposure to UV radiation without adequate protection can significantly increase your risk of developing skin cancer. It is crucial to take measures to shield your skin from harmful UV rays.
How Does UV Exposure Contribute to the Development of Skin Cancer?
UV rays have a profound impact on skin cells, causing damage that can lead to the formation of cancerous growths. Understanding how UV exposure affects the skin is essential for implementing preventive measures.
Impact of UV rays on skin cells
UV rays penetrate the top layers of the skin, causing damage to the DNA of skin cells and potentially triggering mutations that give rise to skin cancer.
Types of skin cancer caused by UV exposure
Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are often linked to chronic sun exposure, while melanoma is more commonly associated with intense, intermittent sun exposure that causes sunburns.
How sun exposure increases your risk of skin cancer
Cancer is the most common in people who are massively exposed to the sun. Repeated sun exposure without protection can lead to cumulative skin damage, increasing the risk of developing various forms of skin cancer over time.
Understanding Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer
Non-melanoma skin cancer, which includes basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, is the most common form of skin cancer. Being aware of its characteristics and risk factors is essential for prevention.
Information about non-melanoma skin cancer
Non-melanoma skin cancer typically develops in the top layer of the skin and is often associated with UV exposure and cumulative sun damage.
Risk factors associated with non-melanoma skin cancer
Individuals with fair skin, a history of sunburns, or prolonged sun exposure are at an increased risk of developing non-melanoma skin cancer compared to people with dark skin. Regular skin checks are crucial for early detection.
Sun protection and prevention of non-melanoma skin cancer
Practicing sun protection measures such as wearing sunscreen, protective clothing, and seeking shade can help reduce the risk of non-melanoma skin cancer. Early detection and treatment are key to managing the disease effectively.
Importance of Skin Cancer Prevention and Early Detection
Preventing skin cancer involves taking proactive steps to protect your skin from UV radiation and being vigilant about any changes that may indicate a potential issue. Early detection through regular skin checks can lead to better treatment outcomes.
Steps to protect your skin from UV radiation
Protecting your skin from UV radiation involves wearing sunscreen, seeking shade during peak sunlight hours, and wearing protective clothing such as hats and sunglasses.
Signs that may lead to skin cancer diagnosis
Changes in existing moles, new skin growths, or persistent sores that do not heal should be evaluated by a dermatologist to rule out skin cancer. Prompt medical attention is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Role of Cancer Council in Skin Cancer Awareness
The Cancer Council plays a pivotal role in raising awareness about skin cancer, promoting sun safety initiatives, and providing resources for skin cancer prevention and early detection. Their position statements and support services are valuable in the fight against this common cancer.
There are many types of skin cancers. Many Australians are burnt on a regular basis, and sunburns are often associated with outdoor activities we spend our leisure time doing, such as outdoor sports, gardening and swimming. Many outdoor workers are also burnt frequently although workplace health and safety prevention has helped to some degree.
-
How do I protect my children against skin cancer?
Sun damage at a young age is potentially the most dangerous, because the skin is thin and delicate and may burn more easily. It is also the time when sunburn is most likely to result in freckling and mole formation, which are both markers for people at risk of future skin cancers. In fact, a mole count over forearms is an indication of future melanoma risk, with high mole counts being associated with increased lifetime risk of melanoma. Children need to be protected from sun damage and in particular sun burn with hats, sunglasses, protective clothing (shirts, rash vests), high potency sunscreens (50+ SPF recommended) and avoidance sun exposure in the hottest part of the day. Every sunburn contributes to an increased risk of skin cancer in future and there may be a very long (decades) delay before the skin cancer appears. Skin cancers occurring after a single sunburn has been documented, with a delay of 40 years between the sunburn and the eventual cancer formation. Regular sunscreen application for skin types susceptible to sun burn can prevent accidental sunburns, and lead to a reduced risk of future skin cancers.
Most children are at very low risk of skin cancers, so regular skin checks are not routinely recommended unless there are particular concerns. While skin cancers including melanoma are rare, they do occur, so if there is a mole or spot that is changing or growing at an accelerated rate, or looks odd or different to every other mole on the child’s body, then they should be checked to ensure it is not a cancer.
Protecting Your Children from Skin Cancer: Sun Protection Tips
Exposure to the sun's harmful UV rays can have detrimental effects on our skin, especially for children whose skin is more delicate and prone to damage. Ensuring proper sun protection for your children is crucial in preventing the risk of skin cancer later in life.
Sun Protection against UV
Why is sun protection important for children? Effective sun protection is essential as children have sensitive skin that is more susceptible to skin damage from UV exposure. Without adequate protection, there is an increased risk of developing skin cancer in the future.
What are the risks of not using sun protection? Not using sun protection exposes children's skin to harmful UV rays, leading to skin damage and an elevated risk of skin cancer development.
How can you effectively protect your child from the sun? Ensuring good sun protection involves a combination of measures such as applying sunscreen regularly, seeking shade, and wearing protective clothing to shield the skin from harmful UV rays.
Sunscreen and Skin Cancer
How does sunscreen help prevent skin cancer? Quality sunscreen forms a protective barrier on the skin, blocking harmful UV rays that can contribute to skin cancer development.
What type of sunscreen is best for children? When choosing sunscreen for children, opt for broad-spectrum formulas with a high UV protection factor to ensure optimal sun protection.
What SPF should you look for in sunscreen? Look for a minimum SPF of 30 or higher to effectively shield your child's skin from damaging UV rays that can lead to skin cancer.
Skin Cancer in Children
What are the signs of skin cancer in children? Watch for unusual moles, sores that don't heal, or changes in existing moles on your child's skin, as these could indicate a potential risk of skin cancer.
How common is skin cancer in children? While less common than in adults, skin cancer can still affect children, making regular skin checks essential for early detection and treatment.
What factors contribute to skin cancer in children? Factors such as UV exposure, type of skin, and sun protection practices play a role in the development of skin cancer in children.
Protective Clothing and Sun Safety for reduced sun exposure
How does protective clothing help in sun protection? Wearing sun protective clothing shields the skin from harmful UV rays, providing an extra layer of defence against skin damage and skin cancer.
What should children wear to stay safe in the sun? Opt for lightweight, long-sleeved shirts, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses to safeguard your child's skin and eyes from UV exposure.
Are there clothing materials that offer better sun protection? Look for fabrics with a tight weave and darker colours, as they offer superior sun protection compared to light-coloured, loosely woven garments.
Sun Protection Measures for Babies and Children
Aside from sunscreen, what other measures can protect children from the sun? Seeking shade during peak UV hours, staying hydrated, and wearing sun-protective clothing are all essential components of comprehensive sun protection measures.
How important are sunglasses in sun protection? Sunglasses not only shield the eyes from UV rays but also reduce the risk of eye damage and skin cancer around the delicate eye area.
Essential awareness of sun protection times
What are the best times to practice sun protection? It is crucial to practice sun protection all year round, especially during summer months and between 10 am and 4 pm when UV levels are at their highest.
Regular Skin Checks
Most children are at very low risk of skin cancers, so regular skin checks are not routinely recommended unless there are particular concerns. While skin cancers, including melanoma, are rare, they do occur, so if there is a mole or spot that is changing or growing at an accelerated rate or looks odd or different to every other mole on the child’s body, then they should be checked to ensure it is not cancer.
-
Sunspots
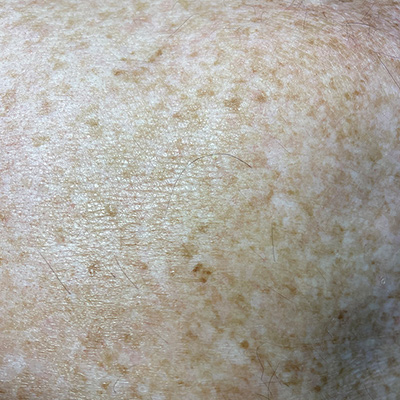
Sunspots, which are also called solar or actinic keratoses, are pink or tan coloured scaly spots that feel slightly rough to the touch. They occur commonly in people over 40 with light skin and hair/eyes and on skin that’s often exposed to the sun. Most common areas are the face, tips of the ears, back of hands and forearms.
-
What is sunburn and how can I prevent it?
Sunburn is the reaction of your skin to exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun. Depending on your skin type and the season, sunburn can occur after as little as ten minutes of sun exposure if adequate protection is not provided. Fair skin types and people with light-coloured hair and eyes are the most prone to sunburn and hence to the subsequent development of skin cancer. Most Australians are aware of the danger of sun exposure, but sunburn is still very common because people underestimate the amount of ultraviolet radiation they are exposing themselves to. This includes days when it is overcast, cooler or windy, when the burning effects of the sun may not be noticed before a sunburn has already happened. All sunburns cause damage to the cells of your skin, and these changes include damage to the DNA of your cells. Over many years, enough damage to the DNA of your cells can accumulate to cause skin cancer to develop. Many older people experience skin cancers many years after the activities that caused them have stopped and may continue to have skin cancers appear from time to time despite minimal sun exposure.
Prevent Sunburn and Skin Cancer with These SunSmart Tips
Sunburn and skin cancer are serious concerns related to sun exposure, especially during the hot summer months. Understanding the symptoms and risks associated with sunburn is crucial for maintaining skin health. By following SunSmart practices and utilising proper sun protection measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of sunburn and skin cancer.
Sunburn Symptoms and Prevention
Recognising the Symptoms of Sunburn
Sunburn is characterised by red, inflamed skin that may feel hot to the touch. It can also cause pain, itching, and tenderness. Severe sunburn may lead to blistering and peeling of the skin, indicating significant damage to the skin cells.
How Can Sunburn Be Prevented?
To prevent sunburn, it is essential to limit sun exposure during peak hours when UV radiation is strongest. Using sunscreen with a high Sun Protection Factor (SPF) and wearing protective clothing, such as hats and sunglasses, can provide additional protection against harmful UV rays.
Effective Sunburn Treatments
If you do get sunburned, it is important to treat your skin gently. Applying cool compresses, moisturizing lotions, and staying hydrated can help soothe the discomfort. Avoiding further sun exposure until the skin heals is crucial to prevent additional damage.
Sunscreen and Sun Protection
Understanding UV Rays and Their Impact
UV rays are a type of radiation from the sun that can penetrate the skin and cause damage. Prolonged exposure to UV rays increases the risk of skin cancer and accelerates skin aging. Understanding the different types of UV rays and their impact on the skin is essential for sun protection.
The Importance of Using Sunscreen
Sunscreen is a vital tool in protecting the skin from harmful UV exposure. It acts as a barrier that absorbs or reflects UV rays, preventing them from penetrating the skin. Regular application of broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF can significantly reduce the risk of sunburn and skin cancer.
Choosing the Right Sun Protection
When selecting sunscreen, look for products with a high Sun Protection Factor (SPF) and broad-spectrum protection that shields against both UVA and UVB rays. Additionally, wearing protective clothing, such as long sleeves and pants, along with sunglasses, further enhances sun protection.
SunSmart and Sun Safety Practices
Reducing the Risk of Sunburn and Skin Cancer
Adopting SunSmart practices is key to minimising the risk of sunburn and skin cancer. This includes seeking shade during peak sun hours, wearing sunscreen, and using protective clothing to shield the skin from harmful UV exposure. Regular skin checks and screenings also help in the early detection of skin issues.
Protecting Your Skin from Harmful UV Exposure
Avoiding excessive sun exposure, especially between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. when UV rays are strongest, is essential for skin protection. Applying sunscreen generously and reapplying every two hours, or after swimming or sweating, ensures continuous UV protection throughout the day.
Utilising SunSmart Strategies for Sun Protection
Utilising SunSmart strategies, such as wearing UV-protective clothing, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses, enhances sun protection. The Cancer Council recommends staying SunSmart by following simple yet effective practices that safeguard your skin from UV damage and reduce the risk of skin cancer.

